Are You Bleeding After Sex?
Any unlooked for bleeding can certainly be worrying, and here are some things to check if you are concerned.
If after having sex with your partner, you look down and see blood on the sheets and it is not your period, it can be worrying.
While vaginal bleeding after sex can be scary, it’s also fairly common and affects up to 9% of menstruating women. There’s probably no cause for concern but it can also result from an infection and in rare cases, it’s a sign of cervical cancer.
What might be causing it?
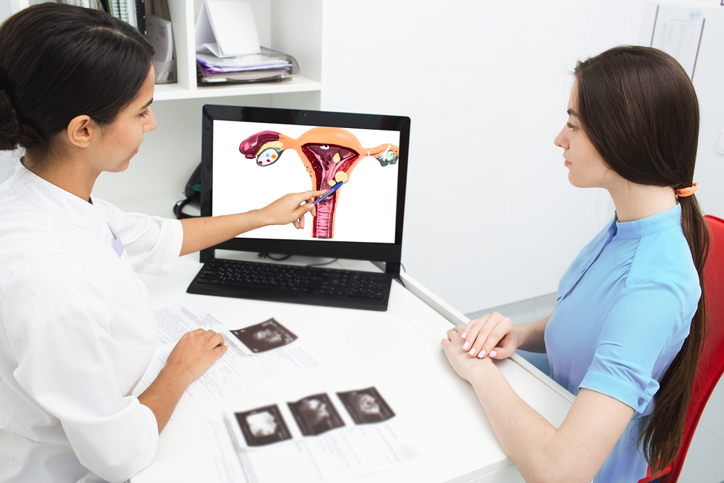
The most common causes for vaginal bleeding after sex both start in the cervix, which is the narrow, tube-like end of your uterus that opens into the vagina.
One of those causes is cervical inflammation, or cervicitis. It can be ongoing and totally harmless, or it can happen because of a sexually transmitted infection that you need to get treated, like chlamydia or gonorrhea. Both types of cervical inflammation can cause bleeding after sex.
A second common reason for bleeding after sex is cervical polyps. These growths are usually small — about 1 to 2 centimeters. They often appear on the opening of your cervix and most aren’t cancerous.
Other causes of vaginal bleeding after sex include:
– Friction during sex or not enough lubrication
– Normal uterine bleeding if you’re just beginning your period or if it’s just ended
– A cervical or vaginal infection
– Sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia and gonorrhoea, which can cause bleeding after sex
– Genital sores caused by herpes or another condition
– A precancerous cervical spot
– Cervical ectropion (when the inner lining of the cervix pokes through the cervical opening and grows on the vaginal side of the cervix)
– Pelvic organ prolapse (when pelvic organs, like the bladder or uterus, protrude or fall just beyond the vaginal walls)
– Cancer of the cervix, vagina, or uterus
Dryness caused by these things can also lead to vaginal bleeding:
– Breastfeeding
– Childbirth
– Some cold, allergy, and anti-oestrogen medications
– Cancer therapy and its effect on your ovaries
– Douching (using water or other liquid to rinse the vagina)
– Sjögren’s syndrome (a chronic autoimmune disorder that happens when the immune system attacks the glands that make moisture in the eyes, mouth, and other parts of the body)
– Menopause
While many of these causes don’t need treatment and are harmless, sometimes vaginal bleeding after sex can be a sign of a more serious problem.
Risk factors
You may have a higher chance of bleeding after sex if you:
– Have cancer of the cervix, vagina, or uterus
– Are going through menopause or perimenopause
– Had a baby not long ago or are breastfeeding
– Aren’t fully aroused before vaginal penetration
– Use douche products
– Have an infected cervix
– Have a sexually transmitted disease or infection
Should I be worried about bleeding after sex?
If you have some minor bleeding every once in a while, chances are everything is fine. But the only way to know for sure is to see your doctor for a physical exam.
If the bleeding happens right before you get your period or within a few days after it ends and it doesn’t happen again, you can hold off on making that appointment.
You can also probably hold off if you recently had a pelvic exam and smear test and got a clean bill of health. In all other cases — or if you’re just worried — it’s best to get checked out to rule out infection or anything more serious.
Bleeding after Menopause
If you’re postmenopausal, any bleeding after sex isn’t normal. See your doctor to rule out cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, and other issues.
Questions your Doctor may ask
Your doctor’s first step will be to see if there’s an obvious cause for the bleeding, like breakthrough bleeding after you just started on a birth control pill.
They’ll also want to know if you’re having pain during sex, which can be a sign of dryness or infection, depending on when it happens.
The doctor will give you a pelvic exam and look for any source of the bleeding, like vaginal tears or lesions, signs of pelvic organ prolapse, cervical polyps, inflammation or a sexually transmitted disease or infection.
Treatment
Since there’s no one cause of bleeding after sex, there’s no single treatment. Some options include:
– Vaginal lubricants and moisturisers
– Medication for sexually transmitted infections
– Oestrogen therapy
– Cervical cancer treatment (surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation)
– Polyp removal
Can it stop on its own?
It might. A recent study found that just over half of women who had bleeding after sex reported that it cleared up on its own within 2 years.
Prevention is always a good idea and you can make some lifestyle changes to lower your risk of bleeding after sex:
– Use a lubricant before and during sex
– Wait a bit longer after your period ends to start having sex again
– Have any cervical polyps or cervical infections treated
– Have more foreplay before penetration
– Try less aggressive sex
Helpful information
This may not be a cause for concern, unless you are postmenopausal, in which case it is always best to have it checked thoroughly.
Vaginal dryness is certainly one element that can be addressed, either by using a combination cream with both progesterone and oestrogen or a separate oestrogen cream as needed and together with balancing progesterone cream.
If low libido is also an issue then the following article will be useful:
https://anna.blog.wellsprings-health.com/are-any-of-these-killing-your-sex-drive/


















